Introduction: Why HCC Coding Matters
Healthcare has made a transition in considering value over volume. This necessitates that providers get adequate reimbursement for the care complexity that is being provided. That is where Hierarchical Condition Category (HCC) coding fits in. HCC coding is at the root of revenue cycle management services in healthcare because it captures patients chronic and complex conditions in such a manner as to influence reimbursement. The codes assist in varying payment in line with patient’s status of health, so that there is proper compensation.
Both government Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) and certain private payers, in risk-adjusted payment, use HCC models. The strategy measures patient complexity, which dictates what providers get in payment. Accurate coding in HCC is critical both financially as well as in support of better care management.
We will break it down further and determine why HCC coding proficiency is paramount to medical billers, coders, and even healthcare providers.
What Is HCC Coding?
HCC coding is a risk-adjustment model that groups diagnosed health conditions into categories; each linked to expected healthcare costs. It was launched by CMS primarily to support Medicare Advantage plans but has since been adopted broadly across various value-based care programs.
Under ICD-10-CM codes submitted by providers, diagnoses get assigned to HCC (Highest Combination of Conditions) categories. Each category is assigned a risk weight, also known as a Risk Adjustment Factor (RAF), which estimates future spending by that patient on healthcare.
Its key contributions to its coding of HCC are:
- CMS: Establishes guidelines, revises models, and enforces compliance.
- Payers and insurers: Reconcile payment and premium with HCC data.
- Clinicians: Report patient status accurately.
- Medical Coders: Translating Clinical Notes into Applicable Codes.
Correct coding of HCC guarantees that the payment system reimburses patient complexity while facilitating effective planning of resources.
How HCC Models Work
HCC models cluster group ICD-10-CM diagnosis codes of equivalent clinical seriousness and anticipated costs by virtue of a hierarchy. Severe diagnoses don't encompass minor ones in the same group to prevent duplicate compensation.
CMS in 2025 follows a hybrid risk adjust model, combining its legacy model of 2020 with its new one, version 28 (V28). The plan is to enhance specificity and precision upon model transition, with complete transition to V28 in 2026.
This is how it works:
1. Diagnosis Capture:
Every documented illness in patient chart is coded in ICD-10-CM.
2. Mapping:
The ICD codes maps to the respective HCC categories.
3. Score Computation:
Each category has a weight that corresponds to costs of treatment, and such weights aggregate in a patient's RAF score.
4. Payment Adjustment:
The RAF score adjusts reimbursed funds by provider based upon patient complexity. The higher the score, the higher payment because more care is anticipated.
For instance, a patient with COPD and diabetes who has complications score higher risk compared to a patient who has a low-level acute condition. These realities affect payment directly, so that's why coding and clinical documentation accurately impact so heavily.
Documentation and Coding Workflow
Accurate coding of HCC is dependent upon concise and accurate clinical documentation. Clinicians must document clearly and support with severity and management notes, all conditions that are applicable as being complex and chronic.
These codes are then applied by coding professionals in awarding risk scores that sufficiently reflect patient complexity. Errors involved in this include vague phrases, missing conditions that are chronic, or use of unspecified codes in ICD-10, which decreases risk scores, therefore underpayment.
Medical coder-provider collaboration enhances capturing of all relevant diagnoses. Periodic coding and documentational quality maintenance training offered by organizations that deal in medical coding services, such as Human medical billing, enhances coding accuracy.
These are a few workflow recommendations for efficient HCC coding:
- Urging doctors to review and correct diagnoses periodically.
- Use coding checklists that are risk adjustment condition oriented.
- Use query processes in conditions of incomplete, unclear, or nonexistent documents.
- Perform regular internal audits to detect codable but uncoded diagnosis (CDI).
- Use denial management services to resolve denied claims due to coding inaccuracies proactively.
Regulatory and Audit Considerations
CMS updates HCC coding guidelines annually, like adding new ICD-10 codes, revising weight assignments, and enhancing categories. One will need to keep it current to avoid penalties or missed revenue.
Both mid-year releases in 2025 and hybrid model include new mappings without deletion, so coding teams must always adapt their strategy.
Common triggers for audit are discrepancies in coded data and medical records or inexplicable changes in risk score. Adherence to guidelines of CMS in a strict manner and performing skilled reviews of invoices deter auditing mistakes and, by extension, claim denial.
Revenue cycle personnel involved in human medical billing also integrate audit functions in billing activities so that claim payment and approval loops become more efficient.
Tools and Technologies Supporting HCC Coding
Artificial intelligence and higher-level analytics came as game-changers in HCC coding work streams. The automated tools read patient charts, detect missing diagnoses, and suggest appropriate codes, as a complement to human expertise.
EHR templates for capturing chronic conditions allow clinicians to input key data to appropriately and accurately capture HCC. In real time, dashboards calculate RAF measures and coding efficiency, revealing opportunities to reach higher accuracy and compliance.
Medical billing for humans incorporates these technologies and experienced coder expertise to provide streamlined medical accounts receivable solutions. This integration decreases mistakes, accelerates reimbursement time, and facilitates scalability as coding sophistication increases.
Best Practices for Achieving Accurate HCC Coding:
Proper coding of HCC requires continued education and clear processes. The following are evidence-based strategies:
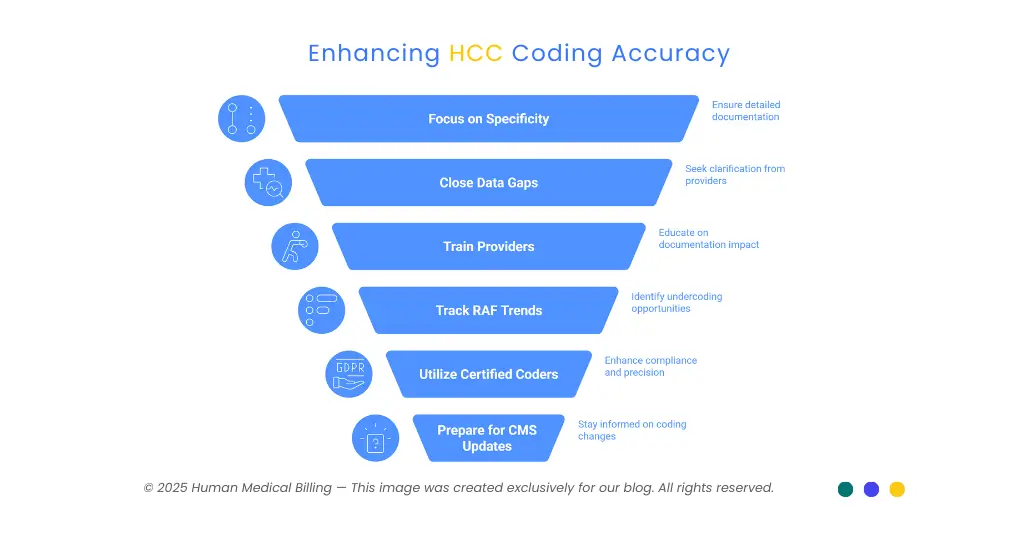
1. Focus on Specificity:
The paper should contain information regarding stage of illness, complications, and current severity.
2. Close the Gap with Questions:
If data are unclear, pose questions to providers early and often obtain more data.
3. Train Providers in Documentation:
Inform clinicians that reimbursement and bedside management directly correlate with what they document.
4. Track RAF Trends:
Comparative studies of past versus current RAFs can uncover undercoding opportunities.
5. Utilize Certified Coders:
Trained staff in medical coding services and risk adjustment enhance compliance and precision.
6. Get Ready for Version 28 Transition:
Find out about CMS updates, new codes, and how it works so that adoption is easy.
Training and Quality Assurance
Continuing coding instruction keeps coding professionals current with new releases of CMS, updates of ICD-10, and risk adjust methodologies. Quarterly seminars as hosts or in affiliation with professional organizations such as Human medical billing enhance coder competency.
Programs of quality assurance must monitor:
- Coding precision percentages
- Trends and variations in RAF score
- Audit pass rate
- Documentation completion
Coaching sessions, performance benchmarks, and feedback loops keep certifications of coders at steady high quality.
Conclusion and Call to Action
It is imperative to understand and proficiently code HCC. It influences appropriate reimbursement that bears resemblance to patient acuity and affects superior care to at-risk communities.
If your organization needs specialized services in medical coding, revenue cycle management of healthcare, or denial management, rely on Human medical billing. Our time-tested solution is a blend of expertise and technology that exploits revenue while maintaining compliance.
See more coding and billing insights and recommendations in our Xpert Billing Blog. Call us at our Contact Us.

