Millions of American children depend on Medicaid to access necessary health services. The planned changes in the federal budget would lower federal spending on Medicaid by more than $1 trillion over a period of ten years, and as much as 11.8 million could lose coverage, including an extensive proportion of children. The following is why stakeholders ought to take notes, what could happen, and how medical providers can plan.
How Medicaid Advances Pediatric Care
Medicaid and the Children's Health Insurance Program (CHIP) insure about 40 percent of American teenagers. These include:
- Preventive vaccinations and screenings
- Mental health screening and treatment
- Certain medicines for chronic illnesses like asthma and diabetes
- Developmental evaluations and therapy services
The Early and Periodic Screening, Diagnostic, and Treatment (EPSDT) benefit guarantees young people access to coverage beyond normal adult coverage. Close to 50 percent of young people who have special health needs rely on Medicaid to obtain therapy and high-tech equipment.
This assistance makes a difference, here's why:
- Upchurch children do not usually have other coverage.
- Early treatment under Medicaid decreases long-term health expenditures.
- Medicaid preventive medicine in childhood reduces ER visits in adult life.
Next steps: think how these possible decreases could shift this picture.
Range of Budget Variations being Suggested
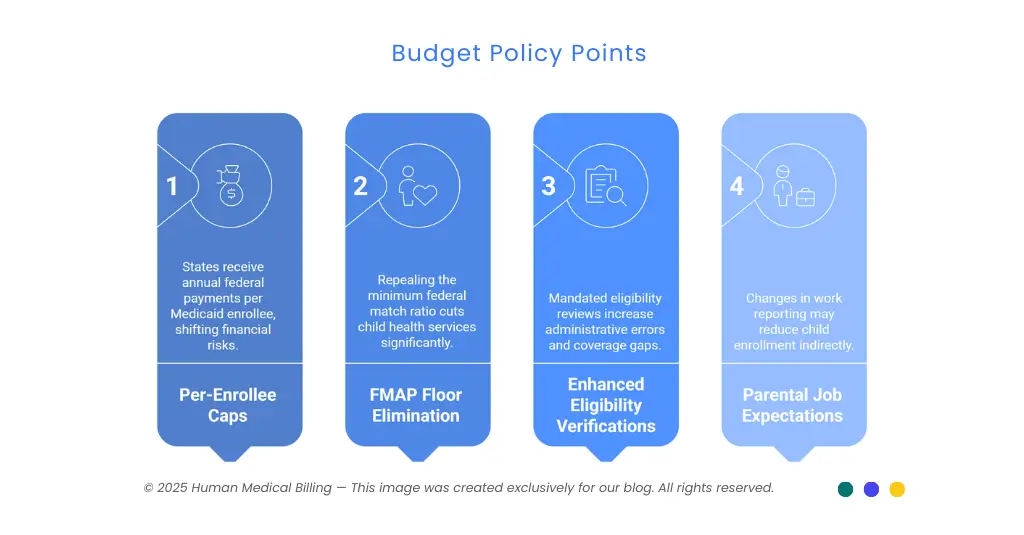
The 2025 budget policy contains several important points:
1. Per-Enrollee Caps:
States would receive an annual federal payment per enrollee in Medicaid. Payments would not increase as spending increases, transferring financial risks to states.
2. FMAP Floor Elimination:
Repeal of the 50 percent federal minimum match ratio would cut child health services by an estimated $57 billion during one decade.
3. Enhanced Eligibility Verifications:
Mandated six-month eligibility reviews for expansion populations in 2027 double today's review rates and raise administrative error likelihood, prompting coverage gaps.
4. Parental Job Expectations:
Changes in work reporting for adult Medicaid participants may reduce enrollment for children indirectly as parents become uncovered.
These steps are proposals until laws have been passed by Congress. The Congressional Budget Office warns state financing of Medicaid would drop significantly if these changes take place.
Financial Strain on Pediatric Providers
Children’s hospitals and pediatric practices depend heavily on Medicaid revenue. Typical figures show:
| Provider Type | Medicaid Share of Patients | Reimbursement vs. Medicare Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Children’s hospitals | 55 percent | N/A |
| Pediatric practices (average) | N/A | 72 percent |
Phoenix Children's Hospital asserts these cuts to supplemental payments to Medicaid would bring losses of $172 million annually. The practices would restrict Medicaid patients, bill families for the cost, or reduce personnel to bridge lower reimbursement rates.
Here is why revenue matters:
- Reimbursements for pediatric services under Medicaid might be lower than practice expenses.
- Supplemental payments reimburse hospitals fixed expenses.
- Budget cuts may result in shutting down programs or downscaling services.
Accessibility Barrier and Quality Impact
Less funding to Medicaid can provide several barriers:
- States can also reduce elective services like mental health services, dental services, and developmental screenings.
- Those eligibility limits might contract, disqualifying families who at present qualify.
- Tough prior authorization requirements may deter treatment involving acute and chronic disease.
Georgetown University research links gaps in coverage of any length to higher emergency room visits among young people. Without access to ongoing care, emergency services come into play at an unsustainable cost to hospital resources and budget.
Next steps for families: research other coverage and regular ongoing provider communication.
Rural and Demographic Disparities
Rural communities disproportionately bear the brunt. The National Rural Health Association threatens pediatric unit shutdowns in rural hospitals due to potential cuts in Medicaid. Families can spend long hours traveling to have care or do without it altogether.
Poor and minority families may lose more in terms of coverage. Studies have shown uninsured poor children have been reported to have:
- Delays in preventive care, leading to adverse health outcomes
- Higher hospitalizations due to treatable condition in outpatient contexts
- Additional absence from school due to untreated disease
Challenges in Revenue Cycle Management in Healthcare
1. Insurance Verification:
Employment changes or changes in family income most often trigger coverage changes.
2. Coding Variations:
Problem-oriented vs preventive CPT codes and modifiers related to age-related visits require specificity.
3. Vaccine Billing:
Every dose and administration of vaccine needs to be separately coded.
4. Denial Risk:
Stringent Medicaid rules increase claim denials.
Specialty billing services can reduce these strains. Medical billing for pediatric practices offers bundled revenue cycle management services for healthcare, denial management services, and medical billing services based on artificial intelligence to optimize pediatric practice revenue streams.
Adapting through Information Technology and Cooperation
Child specialists can build financial strength in:
- Automation of eligibility checks to identify potential gaps in coverage sooner.
- Implementing robust guidelines for documentation to support Medicaid requirements.
- Provision of medical coding services for accurate submission of claims.
- Operating in tandem with medical accounts receivable services to hasten collections.
AI tools allow for errors in claims to be identified prior to submission, minimizing denials and accelerating payments. Future steps for practice involve assessing technology vendors and educating personnel on new workflows.
Long-Term Health Impact on Child Health
Stable coverage in health correlates to positive outcomes throughout life. Children who lose preventive care have:
- Elevated prevalence of chronic disease in adulthood
- Lower academic achievement due to health-related school absences
- Growing healthcare expenses in the long run as untreated illnesses progress
Neutral, Forward-Looking Perspective
This review in no way criticizes any political party or personality. It points out clearly proposed actions await parliamentary endorsements. The providers, families, and state leaders must:
- Monitor congressional activities and public comment periods.
- Engage through professional associations to share information regarding pediatric requirements for treatment.
- Locate other state funding to support core services.
Advice for Providers and Families
- Monitor new bills and shifts in state policy in Medicaid.
- Execute financial analyses to strategize for potential changes in reimbursement.
- Simplify billing process through medical credentialing services as well as medical coding services to reduce denials.
- Get personalized revenue cycle plans from consulting medical billing services such as Human medical billing.
- Refer to materials like our FAQs and how our services work pages to keep updated.
- Refer to Xpert Billing Blog's success stories in dealing with policy changes.
Next steps:
- View our about us and contact us pages to access experts.
- Check out our success stories section to discover how practices thrived despite pressures over funding.
To comprehend how reductions in Medicaid expenditures affect child treatment will enable stakeholders to take better-informed decisions to protect child health. Incorporating advocacy, intelligent financial planning, and professional billing services, pediatric practices can keep providing quality services - regardless of financial uncertainties.

